While measurements made in physics, the terms precision and accuracy are frequently used. They should be distinguished clearly. The precision of a measurement is determined by the instrument or device being used and the accuracy of a measurement depends on the fractional or percentage uncertainty in that measurement.
| For your information |
 We use many devices to measure physical quantities, such as length. Time. And temperature. They all have some limit of precision We use many devices to measure physical quantities, such as length. Time. And temperature. They all have some limit of precision |
Precision and Accuracy Example
For example, When the length of an object is recorded as 25.5 cm by using a meter rod having smallest division in millimeter, it is the difference of two readings of the initial and final positions. The uncertainty in the single reading as discussed before is taken as ± 0.05 cm which is now doubled and is called absolute uncertainty equal to ± 0.1 cm. absolute uncertainty, in fact, is equal to the least count of the measuring instrument.
Precision or absolute uncertainty (least count) = ± 0.1 cm

Another measurement taken by vernier calipers with least count as 0.01 cm is recorded as 0.45 cm.
It has precision or absolute uncertainty (least count) = ± 0.01 cm
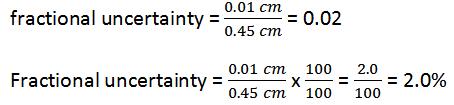
Thus the reading 25.5 cm taken by meter rule is although less precise but is more accurate having less percentage uncertainty or error.
Whereas the reading 0.45 cm taken by vernier calipers is more precise but is less accurate. In fact, it is the relative measurement which is important. The smaller a physical quantity, the more precise instrument should be used. Here the measurement 0.45 cm demands that a more precise instrument, such as micrometer screw gauge, with least count 0.001 cm, should have been used. Hence, we can conclude that:
| For your information |
| Co lour printing uses just four colors – cyan, magenta, yellow and black to produce the entire range or colors. All the colors in this book have been made from just these four colors. |
A precise measurement is the one which has less absolute uncertainty and an accurate measurement is the one which has less fractional or percentage uncertainty or error.
Further Reading:
https://www.webassign.net/userimages/fgdennis@waynecc/lab_app_accuracy.pdf
